It's quite a common practice to use QWebEngineView as a documentation (or document) browser in PyQt5
applications as it allows the documentation to be created using familiar tools. You can build
HTML documentation and bundle it with your application (or host them remotely) then allow your users to browse them within the app.
However, this raises an issue when the document contains links to external resources -- how should these links be handled? It's a weird user experience if your users, through clicking a series of links, can end up on Google or Facebook inside your application. One way to avoid this is to enforce opening of certain links in external windows or browsers, ensuring your documentation browser remains just that.
In this quick tutorial we'll look at how to implement custom link handling in your Qt browser and use this to redirect clicked links to different windows or the user's desktop browser.
The skeleton web browser code is shown below. We'll modify this to add the open in new window behavior.
- PyQt5
- PySide2
from PyQt5.QtCore import QUrl
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PyQt5.QtWebEngineWidgets import QWebEngineView
import os
import sys
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.browser = QWebEngineView()
self.browser.setUrl(QUrl("https://www.mfitzp.com"))
self.setCentralWidget(self.browser)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
app.exec_()
from PySide2.QtCore import QUrl
from PySide2.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PySide2.QtWebEngineWidgets import QWebEngineView
import os
import sys
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.browser = QWebEngineView()
self.browser.setUrl(QUrl("https://www.mfitzp.com"))
self.setCentralWidget(self.browser)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
app.exec_()
This creates our basic browser window and navigates to the LearnPyQt homepage. All links will open within the same browser window (normal browser behavior).
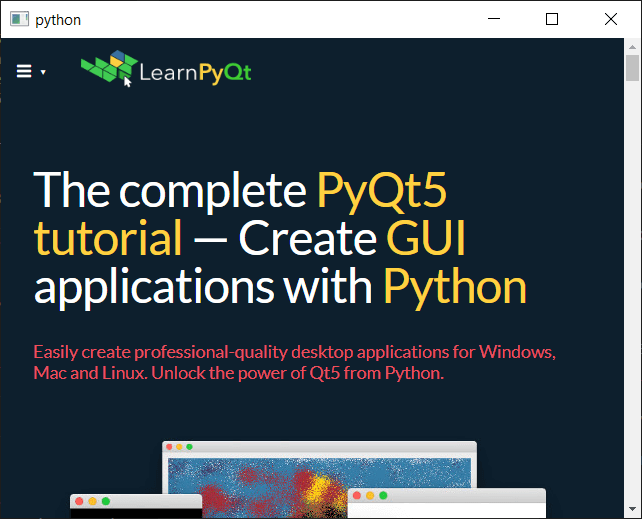 The basic browser window.
The basic browser window.
Popping up a new window for each link
To override the default navigation behavior we need to create a customized QWebEnginePage class. This is the Qt class
which handles viewing (and editing) of web documents, such as web pages within the QWebEngineView.
PyQt/PySide 1:1 Coaching with Martin Fitzpatrick — Save yourself time and frustration. Get one on one help with your Python GUI projects. Working together with you I'll identify issues and suggest fixes, from bugs and usability to architecture and maintainability.
By creating a custom QWebEnginePage class we are able to intercept the .acceptNavigationRequest signal and implement
custom behavior. For example, we can decline links to block navigation, alter the links to navigate somewhere else, or
(as we're doing here) open up custom viewers. In our specific case we will both decline the default behavior,
by returning Falseand implement our own, by opening a new window.
For our new windows, we create a custom web engine view (the same type we have in the main window), set the URL and then
display the window. Note that we need to keep a reference to the created window (in the external_windows list) so it isn’t
destroyed on exiting this method.
For everything else, we pass through to the handler on the parent class with super().acceptNavigationRequest().
from PyQt5.QtWebEngineWidgets import QWebEnginePage
class CustomWebEnginePage(QWebEnginePage):
""" Custom WebEnginePage to customize how we handle link navigation """
# Store external windows.
external_windows = []
def acceptNavigationRequest(self, url, _type, isMainFrame):
if _type == QWebEnginePage.NavigationTypeLinkClicked:
w = QWebEngineView()
w.setUrl(url)
w.show()
# Keep reference to external window, so it isn't cleared up.
self.external_windows.append(w)
return False
return super().acceptNavigationRequest(url, _type, isMainFrame)
To use our custom page class we need to set it on the browser with .setPage().
After this, any navigation is sent through the custom page instance and our
acceptNavigationRequest handler.
self.browser = QWebEngineView()
self.browser.setPage(CustomWebEnginePage(self))
self.browser.setUrl(QUrl("http://google.com"))
The full working example is shown below.
- PyQt5
- PySide2
from PyQt5.QtCore import QUrl
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PyQt5.QtWebEngineWidgets import QWebEngineView, QWebEnginePage
import os
import sys
class CustomWebEnginePage(QWebEnginePage):
""" Custom WebEnginePage to customize how we handle link navigation """
# Store external windows.
external_windows = []
def acceptNavigationRequest(self, url, _type, isMainFrame):
if _type == QWebEnginePage.NavigationTypeLinkClicked:
w = QWebEngineView()
w.setUrl(url)
w.show()
# Keep reference to external window, so it isn't cleared up.
self.external_windows.append(w)
return False
return super().acceptNavigationRequest(url, _type, isMainFrame)
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.browser = QWebEngineView()
self.browser.setPage(CustomWebEnginePage(self))
self.browser.setUrl(QUrl("https://www.mfitzp.com"))
self.setCentralWidget(self.browser)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
app.exec_()
from PySide2.QtCore import QUrl
from PySide2.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PySide2.QtWebEngineWidgets import QWebEngineView, QWebEnginePage
import os
import sys
class CustomWebEnginePage(QWebEnginePage):
""" Custom WebEnginePage to customize how we handle link navigation """
# Store external windows.
external_windows = []
def acceptNavigationRequest(self, url, _type, isMainFrame):
if _type == QWebEnginePage.NavigationTypeLinkClicked:
w = QWebEngineView()
w.setUrl(url)
w.show()
# Keep reference to external window, so it isn't cleared up.
self.external_windows.append(w)
return False
return super().acceptNavigationRequest(url, _type, isMainFrame)
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.browser = QWebEngineView()
self.browser.setPage(CustomWebEnginePage(self))
self.browser.setUrl(QUrl("https://www.mfitzp.com"))
self.setCentralWidget(self.browser)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
app.exec_()
If you run this example and click on a link in the page, a new window will be opened
for every link you click. You can continue to navigate within those external windows
as normal -- they use the standard QWebEnginePage class, so don't have our open in new window behavior.
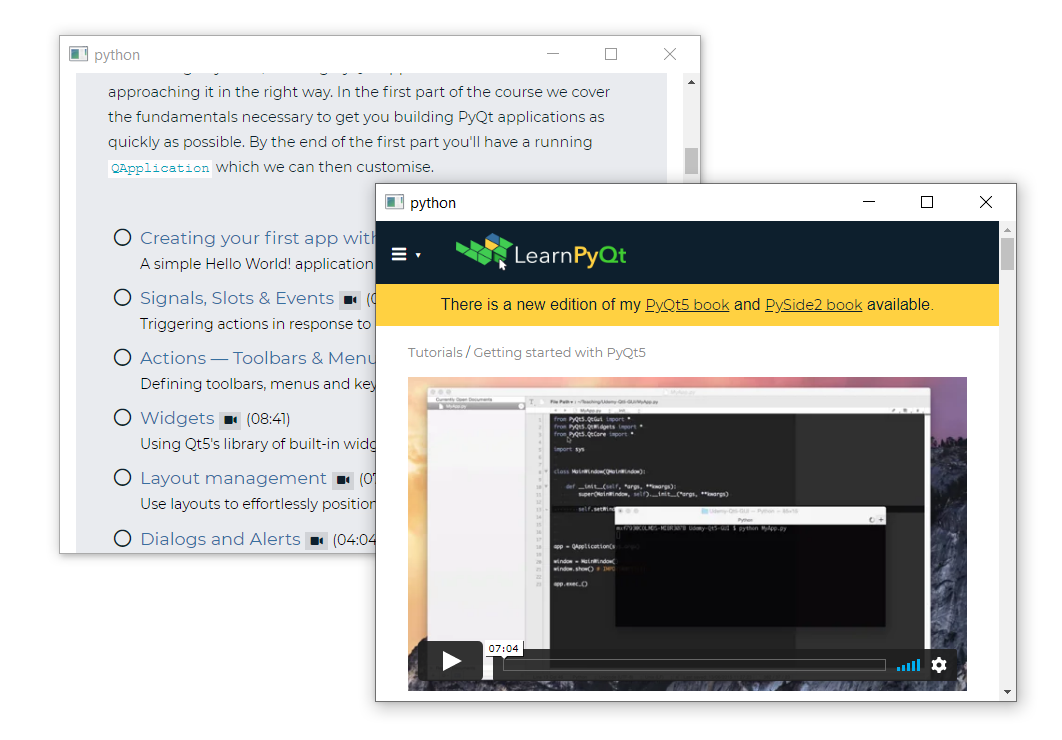 Links are opened in a new window.
Links are opened in a new window.
Conditionally popping up a new window
Sometimes you only want "external" links to be popped up into a separate window -- navigation within your documentation should stay within the documentation browser window, and only external links (not from your documentation) popped up into a separate window.
Since we have access to the URL being navigated this is pretty straightforward. We can
just compare that URL to some pattern (here we're using the hostname via url.host()),
and choose to either pop a new window, or pass it to the default handler.
Purchasing Power Parity
Developers in [[ country ]] get [[ discount.discount_pc ]]% OFF on all books & courses with code [[ discount.coupon_code ]]class CustomWebEnginePage(QWebEnginePage):
""" Custom WebEnginePage to customize how we handle link navigation """
# Store external windows.
external_windows = []
def acceptNavigationRequest(self, url, _type, isMainFrame):
if (_type == QWebEnginePage.NavigationTypeLinkClicked and
url.host() != 'www.mfitzp.com'):
# Pop up external links into a new window.
w = QWebEngineView()
w.setUrl(url)
w.show()
# Keep reference to external window, so it isn't cleared up.
self.external_windows.append(w)
return False
return super().acceptNavigationRequest(url, _type, isMainFrame)
Navigating around the LearnPyQt site now stays within the main browser, but external links (such as to the forum) are popped out into a separate window.
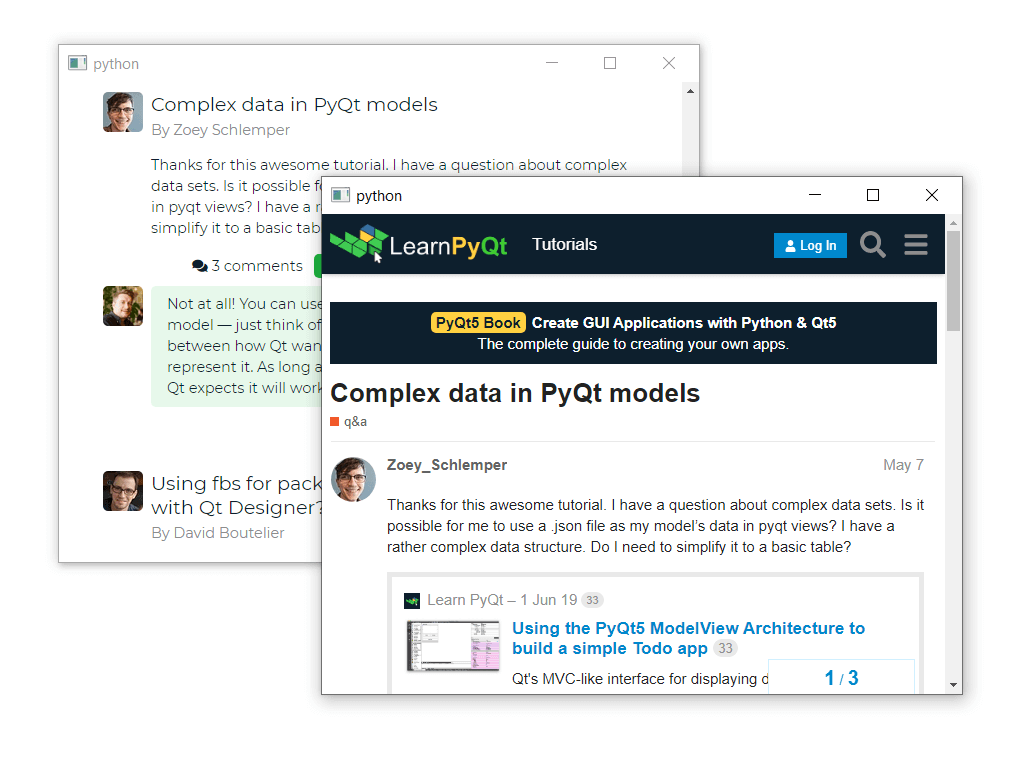 The external window is popped up for external links only.
The external window is popped up for external links only.
Reusing an external window
In this first example we're creating a new window for every link, rather than creating a new window if none exists and then sending all subsequent link clicks to that same window. To get this second behavior we just need to hold a single reference to the external window and check if it exists before creating a new one.
class WebEnginePage(QWebEnginePage):
# Store second window.
external_window = None
def acceptNavigationRequest(self, url, _type, isMainFrame):
print(url, _type, isMainFrame)
if _type == QWebEnginePage.NavigationTypeLinkClicked:
if not self.external_window:
self.external_window = QWebEngineView()
self.external_window.setUrl(url)
self.external_window.show()
return False
return super().acceptNavigationRequest(url, _type, isMainFrame)
Putting this into our example gives us the following complete example.
- PyQt5
- PySide2
from PyQt5.QtCore import QUrl
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PyQt5.QtWebEngineWidgets import QWebEngineView, QWebEnginePage
import sys
class CustomWebEnginePage(QWebEnginePage):
# Store second window.
external_window = None
def acceptNavigationRequest(self, url, _type, isMainFrame):
print(url, _type, isMainFrame)
if _type == QWebEnginePage.NavigationTypeLinkClicked:
if not self.external_window:
self.external_window = QWebEngineView()
self.external_window.setUrl(url)
self.external_window.show()
return False
return super().acceptNavigationRequest(url, _type, isMainFrame)
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.browser = QWebEngineView()
self.browser.setPage(CustomWebEnginePage(self))
self.browser.setUrl(QUrl("https://www.mfitzp.com"))
self.setCentralWidget(self.browser)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
app.exec_()
from PySide2.QtCore import QUrl
from PySide2.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PySide2.QtWebEngineWidgets import QWebEngineView, QWebEnginePage
import sys
class CustomWebEnginePage(QWebEnginePage):
# Store second window.
external_window = None
def acceptNavigationRequest(self, url, _type, isMainFrame):
print(url, _type, isMainFrame)
if _type == QWebEnginePage.NavigationTypeLinkClicked:
if not self.external_window:
self.external_window = QWebEngineView()
self.external_window.setUrl(url)
self.external_window.show()
return False
return super().acceptNavigationRequest(url, _type, isMainFrame)
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.browser = QWebEngineView()
self.browser.setPage(CustomWebEnginePage(self))
self.browser.setUrl(QUrl("https://www.mfitzp.com"))
self.setCentralWidget(self.browser)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
app.exec_()
When clicking on a link in the browser window a new window is created. You can browse in that window as normal, but if you click a new link in the parent window, the current page will be replaced with that link.
Opening links in the user's default browser
You might also want to consider popping up external links in the users default browser. This allows them to bookmark the links, or browse as normally, rather than in the restricted browser view your app provides.
For this we don't need to create a window, we can just send the url to the
system default handler. This is accomplished by passing the url to the
QDesktopServices.openUrl() method. The full working example is shown below.
- PyQt5
- PySide2
from PyQt5.QtCore import QUrl
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PyQt5.QtWebEngineWidgets import QWebEngineView, QWebEnginePage
from PyQt5.QtGui import QDesktopServices
import os
import sys
class CustomWebEnginePage(QWebEnginePage):
""" Custom WebEnginePage to customize how we handle link navigation """
# Store external windows.
external_windows = []
def acceptNavigationRequest(self, url, _type, isMainFrame):
if (_type == QWebEnginePage.NavigationTypeLinkClicked and
url.host() != 'www.mfitzp.com'):
# Send the URL to the system default URL handler.
QDesktopServices.openUrl(url)
return False
return super().acceptNavigationRequest(url, _type, isMainFrame)
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.browser = QWebEngineView()
self.browser.setPage(CustomWebEnginePage(self))
self.browser.setUrl(QUrl("https://www.mfitzp.com"))
self.setCentralWidget(self.browser)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
app.exec_()
from PySide2.QtCore import QUrl
from PySide2.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PySide2.QtWebEngineWidgets import QWebEngineView, QWebEnginePage
from PySide2.QtGui import QDesktopServices
import os
import sys
class CustomWebEnginePage(QWebEnginePage):
""" Custom WebEnginePage to customize how we handle link navigation """
# Store external windows.
external_windows = []
def acceptNavigationRequest(self, url, _type, isMainFrame):
if (_type == QWebEnginePage.NavigationTypeLinkClicked and
url.host() != 'www.mfitzp.com'):
# Send the URL to the system default URL handler.
QDesktopServices.openUrl(url)
return False
return super().acceptNavigationRequest(url, _type, isMainFrame)
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.browser = QWebEngineView()
self.browser.setPage(CustomWebEnginePage(self))
self.browser.setUrl(QUrl("https://www.mfitzp.com"))
self.setCentralWidget(self.browser)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
app.exec_()
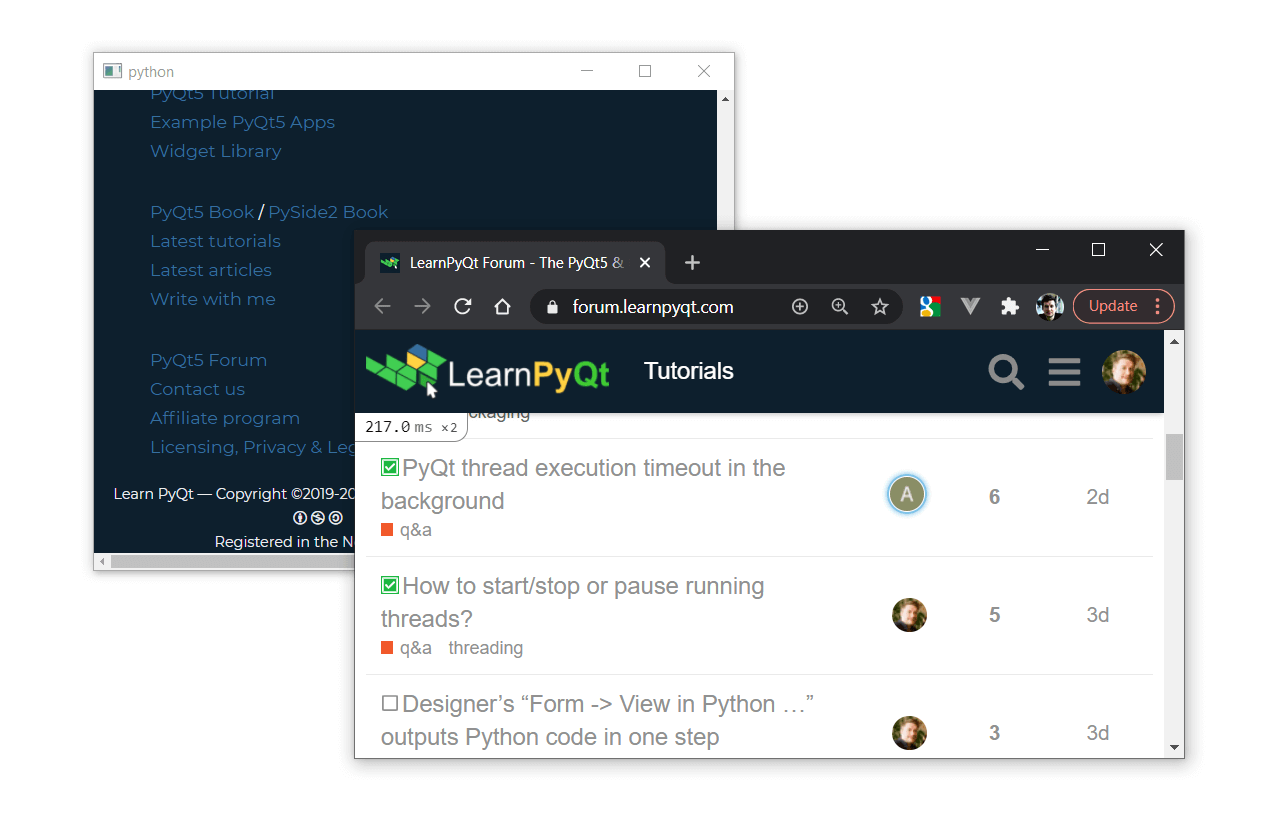
If you run this and click on any external links, you'll see them open in your system's default browser window (here showing Chrome).
Create GUI Applications with Python & Qt6 by Martin Fitzpatrick — (PyQt6 Edition) The hands-on guide to making apps with Python — Over 15,000 copies sold!

